包含TensorFlow中BasicRNNCell,BasicLSTMCell等的实现
1.BasicRNNCell
基本结构如图: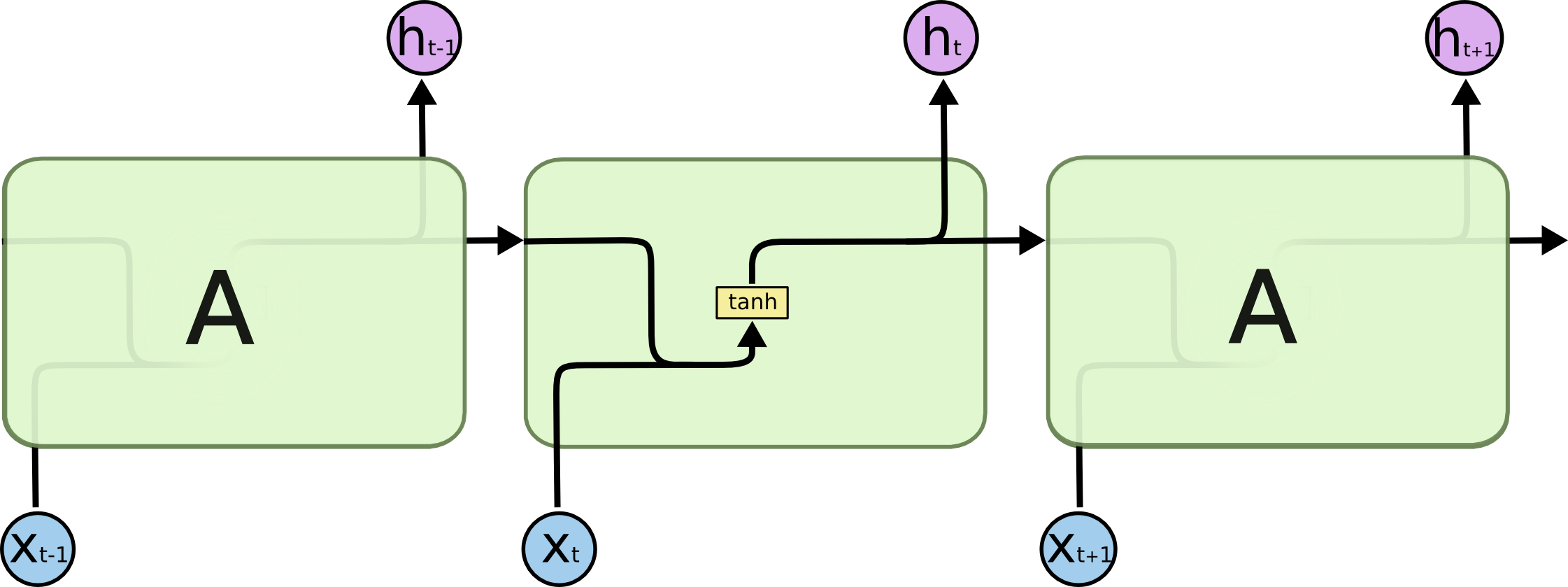
在TensorFlow中,BasicRNNCellm每一步输出的state和output相同,源代码如下:
1 | def call(self, inputs, state): |
公式如下:
或
但是我个人认为应该是:
我也不知道为啥会都写作上面那两种形式.
eg:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
batch_size = 3
input_dim = 2
output_dim = 4
inputs = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, input_dim))
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicRNNCell(num_units=output_dim)
previous_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
output, state = cell(inputs, previous_state)
kernel = cell.variables
X = np.ones(shape=(batch_size, input_dim))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
output, state, kernel = sess.run([output, state,kernel], feed_dict={inputs: X})
print(X.shape)
print(kernel[0].shape)
print(kernel[1].shape)
print(previous_state.shape)
print(state.shape)
print(output.shape)
结果为:
(3, 2)
(6, 4)
(4,)
(3, 4)
(3, 4)
(3, 4)
分析: (kernel中是所有参数的list,此处是W和bias)根据公式(1),$output=([X,previous_state] * W+bias),即([(3, 2);(3, 4)]*(6, 4)+(4,)) = (3,4)$,代码中也较容易看出.
普通RNN梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题原因:
这是一个普通RNN图,其中$W_1$、$W_2$、$W_3$是不同时间步骤下的参数,我们要训练的就是这个参数,输出表达式为:求$W_1$的梯度:
这个讲解的相当清楚
若使用sigmoid函数,则每一次偏导都是一个(0,1)的数
- 初始化W全都(0,1),那么上诉公式中每一个因式都是(0,1),因此连乘的多了就会梯度消失
- 初始化W很大,大到乘以sigmoid函数后还是大于1,那么连乘的多了就会梯度爆炸
2.BasicLSTMCell
基本结构如图: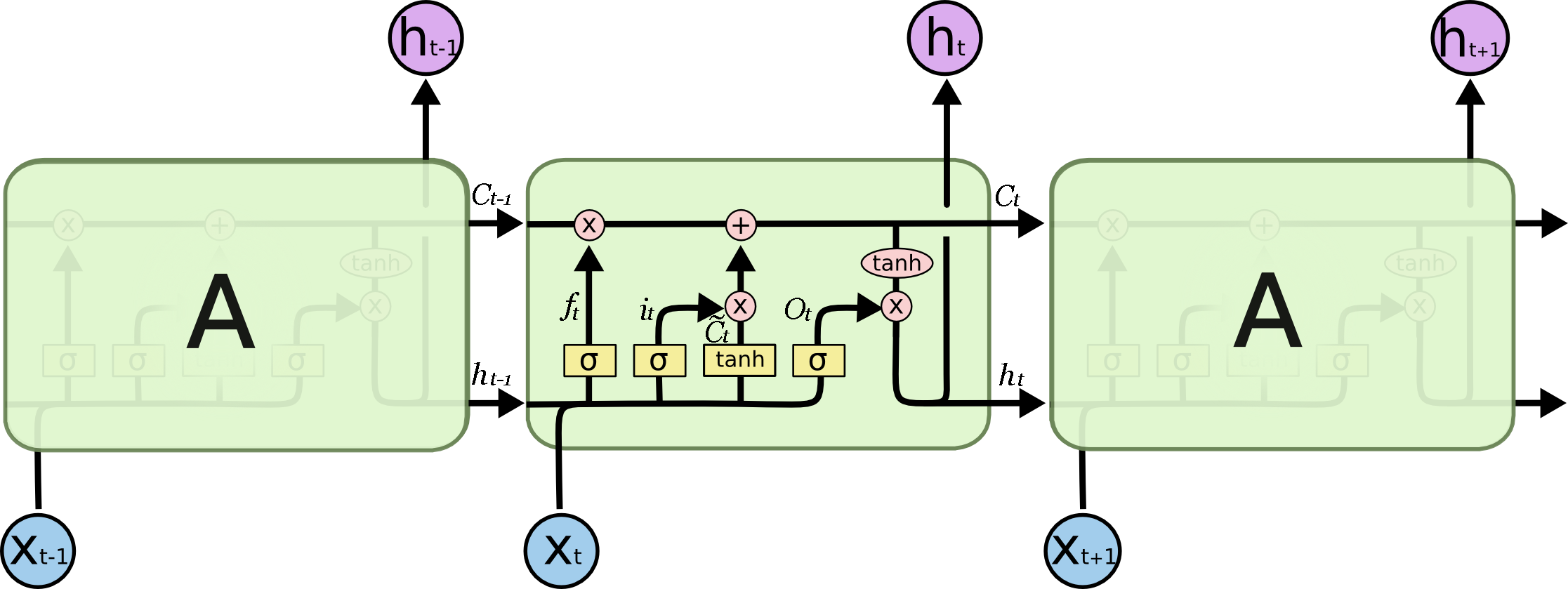
源码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Long short-term memory cell (LSTM).
Args:
inputs: `2-D` tensor with shape `[batch_size, input_size]`.
state: An `LSTMStateTuple` of state tensors, each shaped
`[batch_size, self.state_size]`, if `state_is_tuple` has been set to
`True`. Otherwise, a `Tensor` shaped
`[batch_size, 2 * self.state_size]`.
Returns:
A pair containing the new hidden state, and the new state (either a
`LSTMStateTuple` or a concatenated state, depending on
`state_is_tuple`).
"""
sigmoid = math_ops.sigmoid
one = constant_op.constant(1, dtype=dtypes.int32)
# Parameters of gates are concatenated into one multiply for efficiency.
if self._state_is_tuple:
c, h = state
else:
c, h = array_ops.split(value=state, num_or_size_splits=2, axis=one)
gate_inputs = math_ops.matmul(
array_ops.concat([inputs, h], 1), self._kernel)
gate_inputs = nn_ops.bias_add(gate_inputs, self._bias)
# i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate
i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(
value=gate_inputs, num_or_size_splits=4, axis=one)
forget_bias_tensor = constant_op.constant(self._forget_bias, dtype=f.dtype)
# Note that using `add` and `multiply` instead of `+` and `*` gives a
# performance improvement. So using those at the cost of readability.
add = math_ops.add
multiply = math_ops.multiply
new_c = add(multiply(c, sigmoid(add(f, forget_bias_tensor))),
multiply(sigmoid(i), self._activation(j)))
new_h = multiply(self._activation(new_c), sigmoid(o))
if self._state_is_tuple:
new_state = LSTMStateTuple(new_c, new_h)
else:
new_state = array_ops.concat([new_c, new_h], 1)
return new_h, new_state
公式如下:
同理,我感觉应该是:
eg:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
batch_size = 3
input_dim = 2
output_dim = 4
inputs = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, input_dim))
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=output_dim)
previous_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
output, state = cell(inputs, previous_state)
kernel = cell.variables
X = np.ones(shape=(batch_size, input_dim))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
output, state,kernel = sess.run([output, state, kernel], feed_dict={inputs: X})
print(X.shape)
print(previous_state[0].shape)
print(previous_state[1].shape)
print(kernel[0].shape)
print(kernel[1].shape)
print(state[0].shape)
print(state[1].shape)
print(output.shape)
结果:
(3, 2)
(3, 4)
(3, 4)
(6, 16)
(16,)
(3, 4)
(3, 4)
(3, 4)
分析: (kernel是所有参数,即W和bias)根据上诉公式,在源码中求遗忘门:$f_t$,输入门$i_t$和$\widetilde C_t$s输出门$O_t$的代码为:
i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(value=gate_inputs, num_or_size_splits=4, axis=one)
这里也解释了为什么eg中kernel[0]是(6,16),因为代码中是将4个W同时初始化在一起,即(6,16)中其实是有4个W,并在上诉代码中分别计算,kernal[1]同理。这样得到的i,j,f,o应该都是(3,4),在源码中可以看出计算i,j,f,o是矩阵相乘,但是计算$C_t$和$h_t$是各个元素相乘,因此得到的$C_t$和$h_t$都是(3,4).
3.GRU
源代码为:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Gated recurrent unit (GRU) with nunits cells."""
gate_inputs = math_ops.matmul(
array_ops.concat([inputs, state], 1), self._gate_kernel)
gate_inputs = nn_ops.bias_add(gate_inputs, self._gate_bias)
value = math_ops.sigmoid(gate_inputs)
r, u = array_ops.split(value=value, num_or_size_splits=2, axis=1)
r_state = r * state
candidate = math_ops.matmul(
array_ops.concat([inputs, r_state], 1), self._candidate_kernel)
candidate = nn_ops.bias_add(candidate, self._candidate_bias)
c = self._activation(candidate)
new_h = u * state + (1 - u) * c
return new_h, new_h
eg:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
batch_size = 3
input_dim = 2
output_dim = 4
inputs = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, input_dim))
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell(num_units=output_dim)
previous_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
output, state = cell(inputs, previous_state)
kernel = cell.variables
X = np.ones(shape=(batch_size, input_dim))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
output, state, kernel = sess.run([output, state, kernel], feed_dict={inputs: X})
print(X.shape)
print(previous_state.shape)
print(kernel[0].shape)
print(kernel[1].shape)
print(kernel[2].shape)
print(kernel[3].shape)
print(state.shape)
print(output.shape)
结果:
(3, 2)
(3, 4)
(6, 8)
(8,)
(6, 4)
(4,)
(3, 4)
(3, 4)
